 What is digital identity and why do we need to protect it, in Pakistan of all the places? With globalization and outsourcing on the rise privacy andIdentity theft is fast becoming a global problem. Here are a few reasons for concern regarding privacy and data protection in Pakistan: rise in banking and consumer credit industry, surging number of telecom subscribers, outsourced data processing and grwoth of E-commerce transactions. I’ll provide some background, discuss the existing rules and provide recommendations for business organizations.
What is digital identity and why do we need to protect it, in Pakistan of all the places? With globalization and outsourcing on the rise privacy andIdentity theft is fast becoming a global problem. Here are a few reasons for concern regarding privacy and data protection in Pakistan: rise in banking and consumer credit industry, surging number of telecom subscribers, outsourced data processing and grwoth of E-commerce transactions. I’ll provide some background, discuss the existing rules and provide recommendations for business organizations.The question is: do we have adequate identity and privacy protection in Pakistan? Are banks and telecom companies doing enough to keep your personal information safe? As one example, I was sent phone bills of someone else via e-mail and even after reporting the issue there was no followup. Probably similar incidents have happened with others in Pakistan as well, though statistics are not readily available.
My prediction is that gradually Asian societies (Pakistan, China, India etc) will become more sensitive to data protection and privacy issues. Now is a good time to demand good security practices to safeguard our data.
As a related item I’ll mention theITU Internet Report entitled “digital.life” (in pdf), which was prepared for ITU TELECOM World 2006 . The report examines how innovation in digital technology is radically changing individual and societal lifestyles.
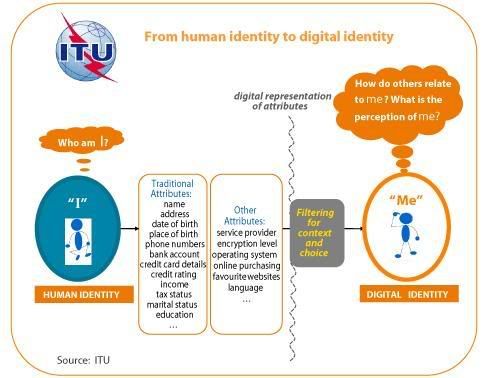
Chapter four, identity.digital, explores the changing nature of the digital individual and the need for greater emphasis on the creation and management of digital identity. Individuals today spend more and more time using digital means to communicate and transact, be that sending and receiving e-mail, talking on a mobile phone, participating in a social networking site, buying music, booking vacations over the internet, or playing an online game. The complexity of the interaction between technology, personal consumption and the construction of identity in the virtual space is a growing area of research. Users of digital technologies have a wide scope for constructing their virtual identity.
What are the laws for data and privacy protection in Pakistan? I found a final draft of the Electronic Data Protection Act 2005 at Pakistan Software Export Board [PSEB] website. It is a relatively short and simple document which provides very basic rules over data collection, processing and handling. The Act tries to solve two problems: a) provide guidelines for outsourced data processing and b) data collection regulation in Pakistan. To give you a flavour of this Act here are 2 definitions from it:
“Sensitive Data” means data revealing racial or ethnic origin, religious, philosophical or other beliefs, political opinions, membership in political parties, trade unions, organizations and associations with a religious, philosophical, political or trade-union, or provide information as to the health or sexual life of an individual and financial, or proprietary confidential corporate data.Electronic data security. Electronic data that is subject to data processing shall be kept under custody, controlled or processed in such a way as to minimize the risks of its destruction or loss, even accidental, unauthorized access, unlawful processing or processing for purposes other than those for which the electronic data were collected, by means of appropriate precautionary security measures.
I would like to hear more from those who are involved in data processing in Pakistan and get some stats about security breaches and their resolution. A few years ago there was some uproar in the US about a data processing company in Pakistan but that issue was settled. Perhaps that incident also contributed to the implementation of Electronic Data Protection Act 2005.
What is the situation in the developed (or G7) world? European Union has stricter standards than US, where laws vary from state to state. The privacy legislation in California is worth mentioning here. State of California is considered by many to be the most strict regarding privacy and identity issues. California has setup a privacy office for this purpose and you can find the legislature details here .
Based on California’s laws Forrester Research recommends the following practices for Business organizations – these recommendations can be applied to any organization:
Pick a framework. The establishment of reasonable security is best built on a foundation that is recognized and accepted. ISO17799 is currently the leading and most accepted framework to build an information security program around. The framework provides a standard architecture to document controls and make sure that everything is covered.
Identify and classify information. The focus of reasonable security is around personal California resident data. Security is first established by classifying this data — define it, assign information owners, establish controls —and identifying where in the organization this information resides. Personal data may be classified into subcategories such as employee data and customer/client data.
Determine business partners that touch your data. Identify which business partner relationships touch and store personal data; this is a critical element that is directly addressed in the legislation. Your organization’s liability does not stop with organizational boundaries — you are required to see adequate security is established in third-party relationships.
Document controls. Utilizing the framework as a structure, the next step is to document the detailed controls in place to line up with the framework. This gets into the depth of defining your policy, operational, contractual, and technical controls in place to protect personal information.
Validate controls. Establishing reasonable security does not stop with documenting controls. In fact, documenting controls that you do not have in place may only open the doors of liability wider. It is necessary to demonstrate that controls are implemented and working as defined in your security control architecture.
A few words about outsourcing and data security. As more firms enter into outsourcing agreements, liability coverage especially for data security and protection becomes more critical. While outsourcers are unlikely to accept unlimited liability, customer organizations can insert limits of liability into their contracts and receive cost reimbursement for any incidents that the outsourcer is responsible for, if they are willing to aggressively negotiate. However, customers must be aware of the real consequences and costs associated with enforcing these clauses or they may find that these clauses have very little real impact. Customers need to protect themselves in outsourcing agreements, but they must balance those needs with realistic expectations from their vendor.

No comments:
Post a Comment